How Internet Archive Preserves Petabytes of Data
How Internet Archive Preserves Petabytes of Data
Fifth Elephant
July 27, 2012
Presenter Notes
The Internet Archive

The Internet Archive
http://www.flickr.com/photos/blmurch/5079018246/Presenter Notes
Internet Archive
Presenter Notes
What is the average lifetime of a URL?
Presenter Notes
What is the average lifetime of a URL?
-
“…estimates put the average lifetime for a URL at 44 days.”
Brewster Kahle "Preserving the Internet" Scientific American, 1997 http://www.sciam.com/0397issue/0397kahle.html
Presenter Notes
What is the average lifetime of a URL?
-
“…estimates put the average lifetime for a URL at 44 days.”
Brewster Khale "Preserving the Internet" Scientific American, 1997 http://www.sciam.com/0397issue/0397kahle.html -
“44% of the sites available on the internet in 1998 had vanished one year later“
Presenter Notes
Preserving the Internet in the Wayback Machine

Presenter Notes
archive.org in 1997
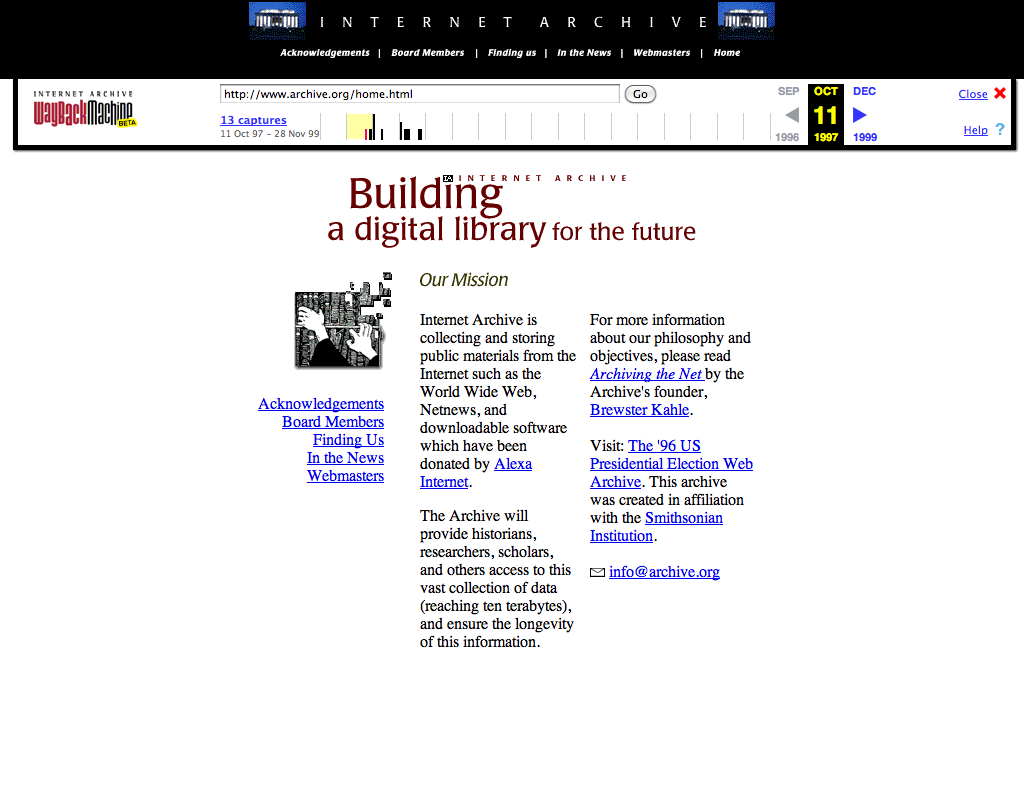
archive.org in 1997
Presenter Notes
Sun CEO Blog in the Wayback Machine

Presenter Notes
The Way Back Machine
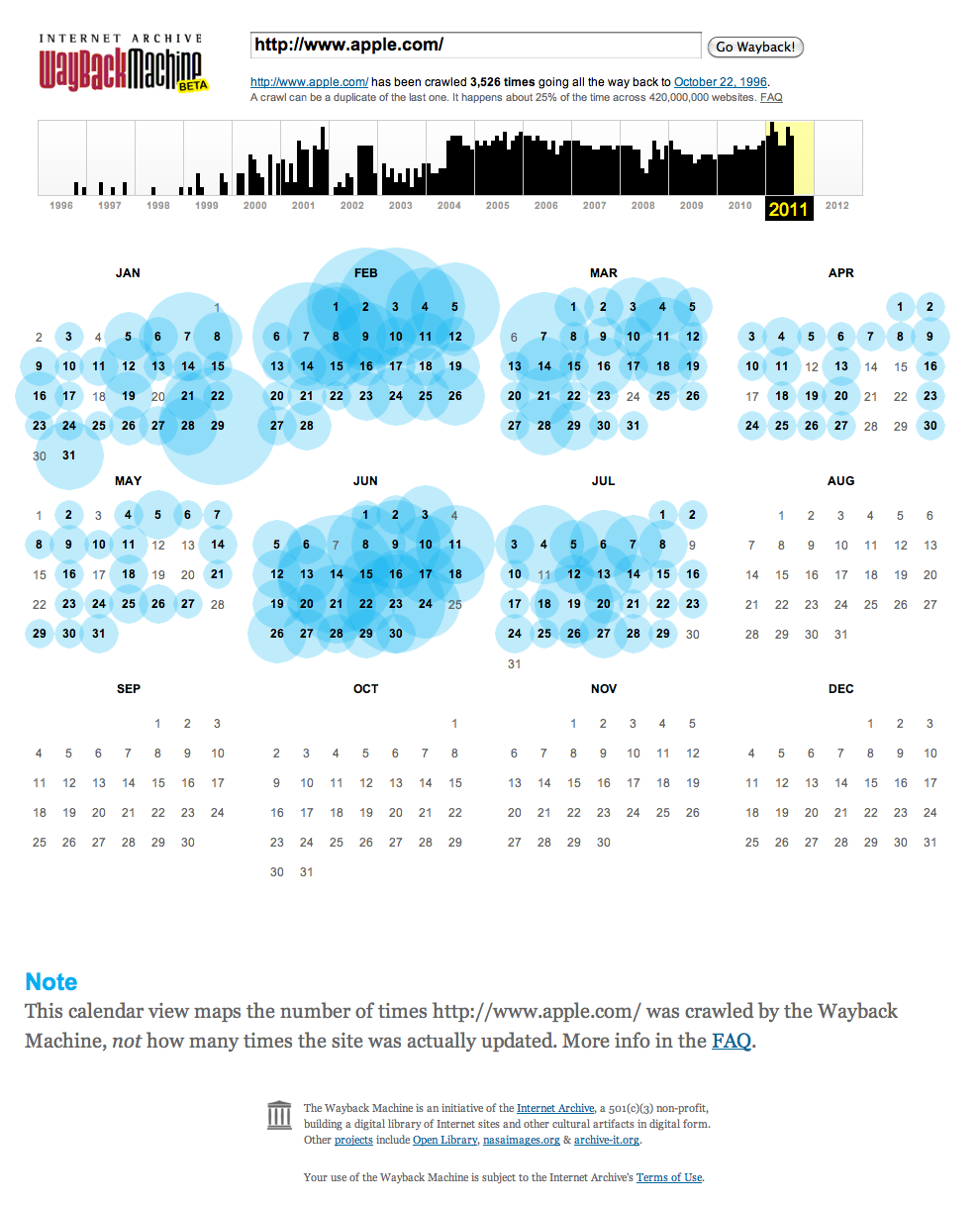
Presenter Notes
www.apple.com - 1996

Presenter Notes
www.apple.com - 1997

Presenter Notes
www.apple.com - 1998

Presenter Notes
www.apple.com - 1999
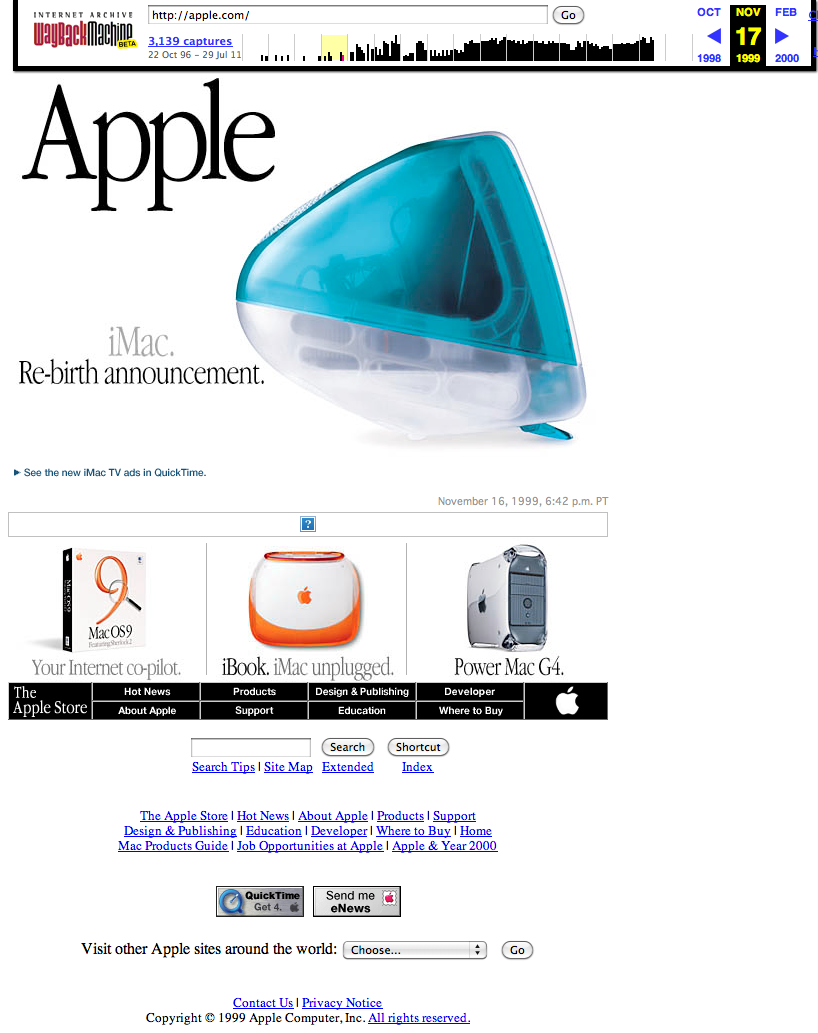
Presenter Notes
www.apple.com - 2000

Presenter Notes
www.apple.com - 2001
Presenter Notes
www.apple.com - 2002
Presenter Notes
www.apple.com - 2003
Presenter Notes
www.apple.com - 2004
Presenter Notes
www.apple.com - 2005
Presenter Notes
www.apple.com - 2006
Presenter Notes
www.apple.com - 2007
Presenter Notes
www.apple.com - 2008
Presenter Notes
www.apple.com - 2009
Presenter Notes
www.apple.com - 2010
Presenter Notes
www.apple.com - 2011

Presenter Notes
Archive It!
Presenter Notes
IA Scanning Center At San Francisco
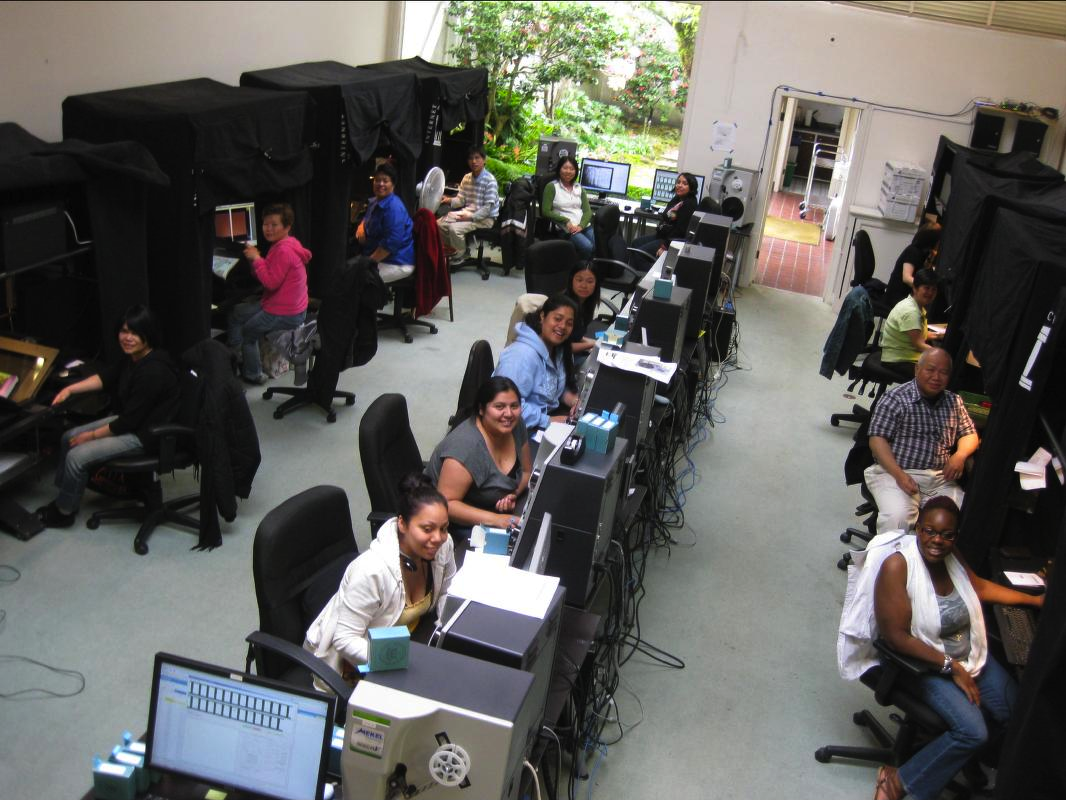

Presenter Notes
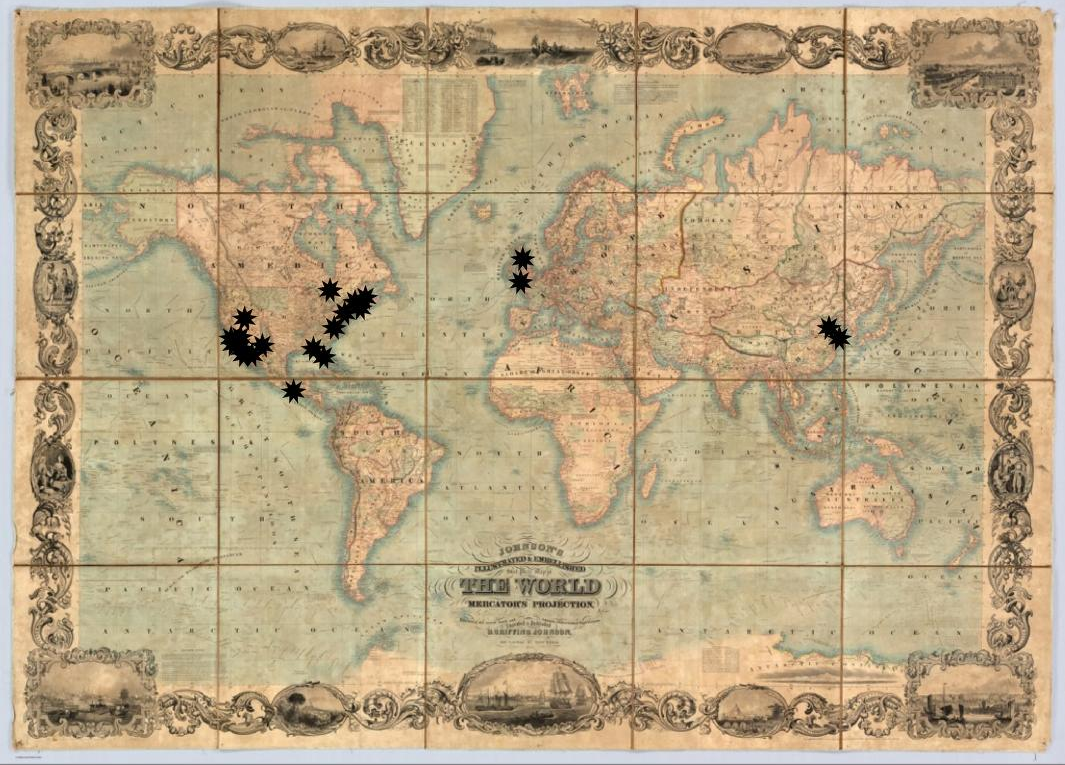
IA Scanning Centers World Wide
Presenter Notes
http://openlibrary.org/
Presenter Notes
Sample Book
Presenter Notes
Fulltext Search
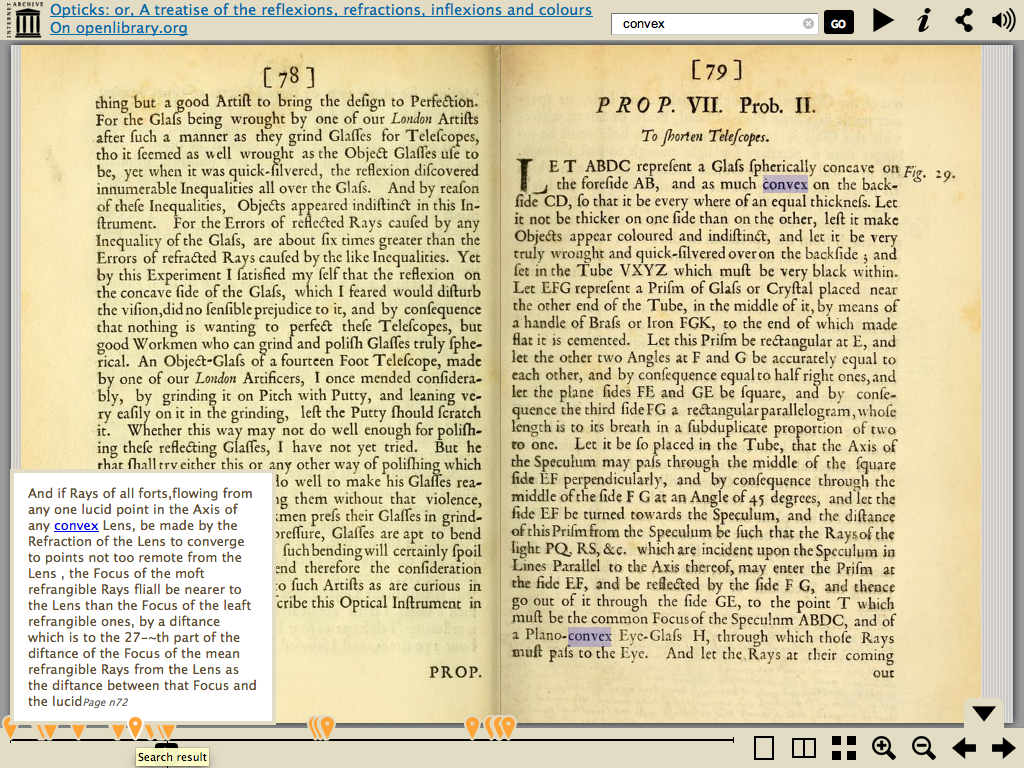
Presenter Notes
Table of Contents

Presenter Notes
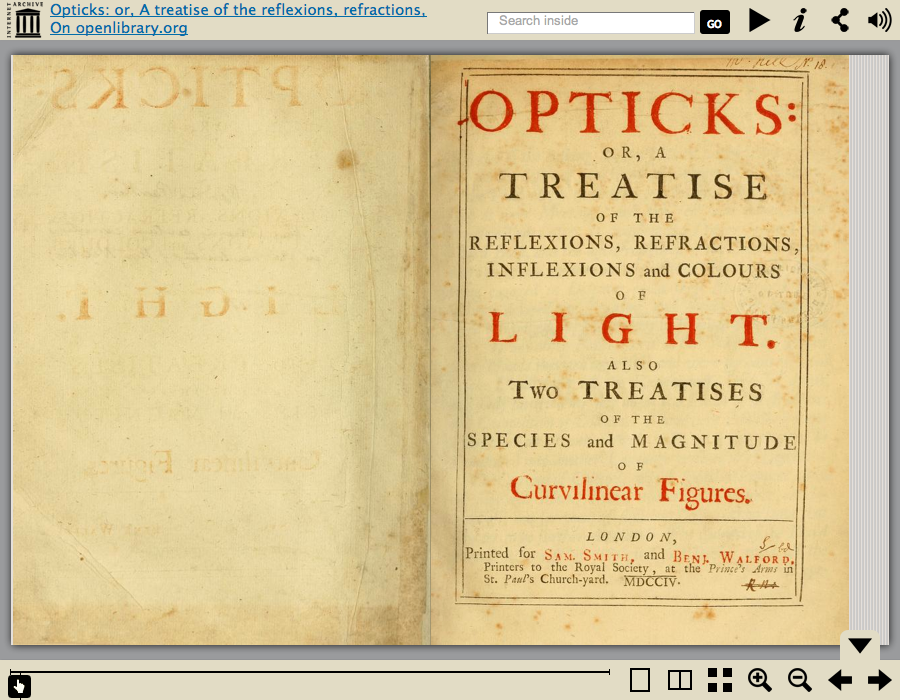
IA Book Reader
The book reader can be embedded in any web page.
Presenter Notes
Newton's Notes


Presenter Notes
Internet Archive
http://archive.org/
Presenter Notes
Universal Access to All Knowledge
Presenter Notes
Big Data
- 3.5 million books
- 170+ billion web pages
- More than 6 Petabytes of data
Presenter Notes
Items
- Fundamental unit of storage.
- The archive is basically a large collection of items (10 million+).
- A directory tree consisting of
- Original files
- Derivatives
- XML Metadata
- Each item is stored on two servers for redundancy.
Presenter Notes
Item example
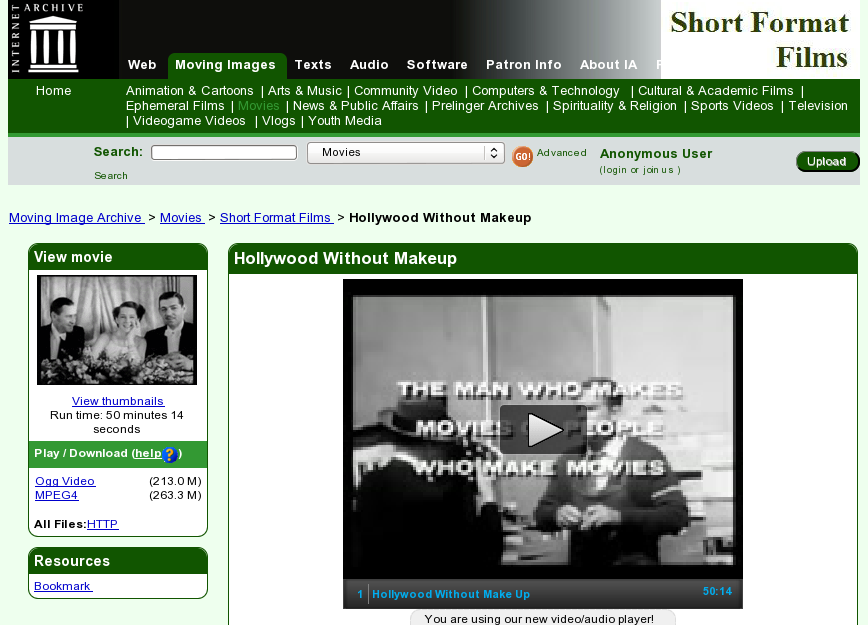
Presenter Notes
Item example
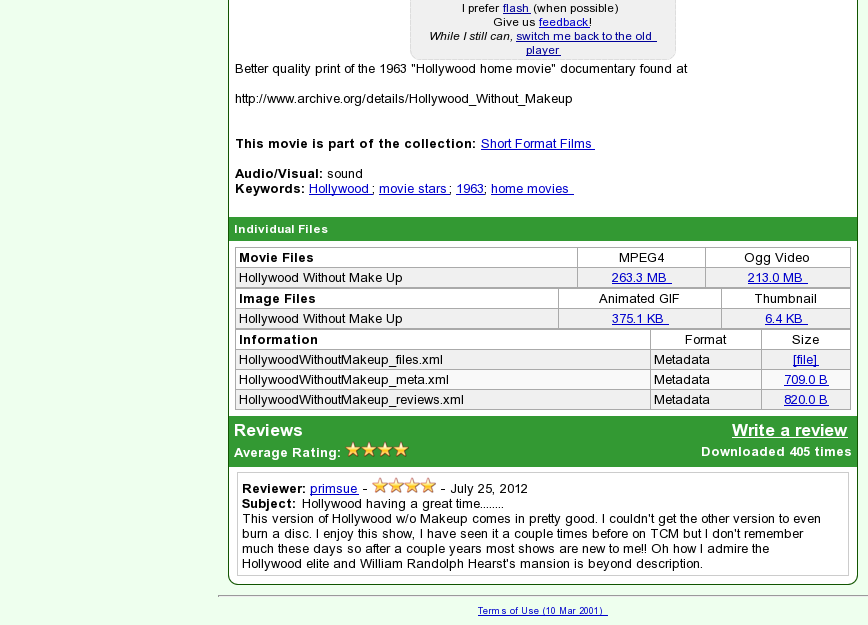
Presenter Notes
Collections
Collectionsare groups of items.- Used for classification.
Presenter Notes
Collection example
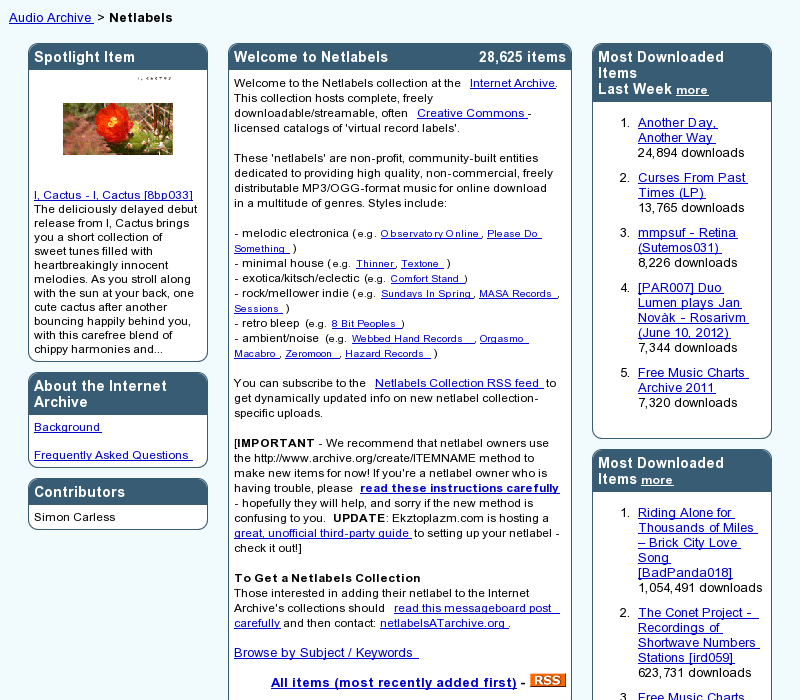
Presenter Notes
Hardware
- The petabox - Designed originally to hold 1 petabyte of data.
- Custom built by the Archive.
- Low power : 6KW per rack,
- High density : 650+ TB per rack
- No air conditioning
- Fits in a shipping container.
- Currently 4 data centres - 1300 nodes, 11000 spinning disks
Presenter Notes
Petabox 1

The first gen petabox
Presenter Notes
Petabox 2
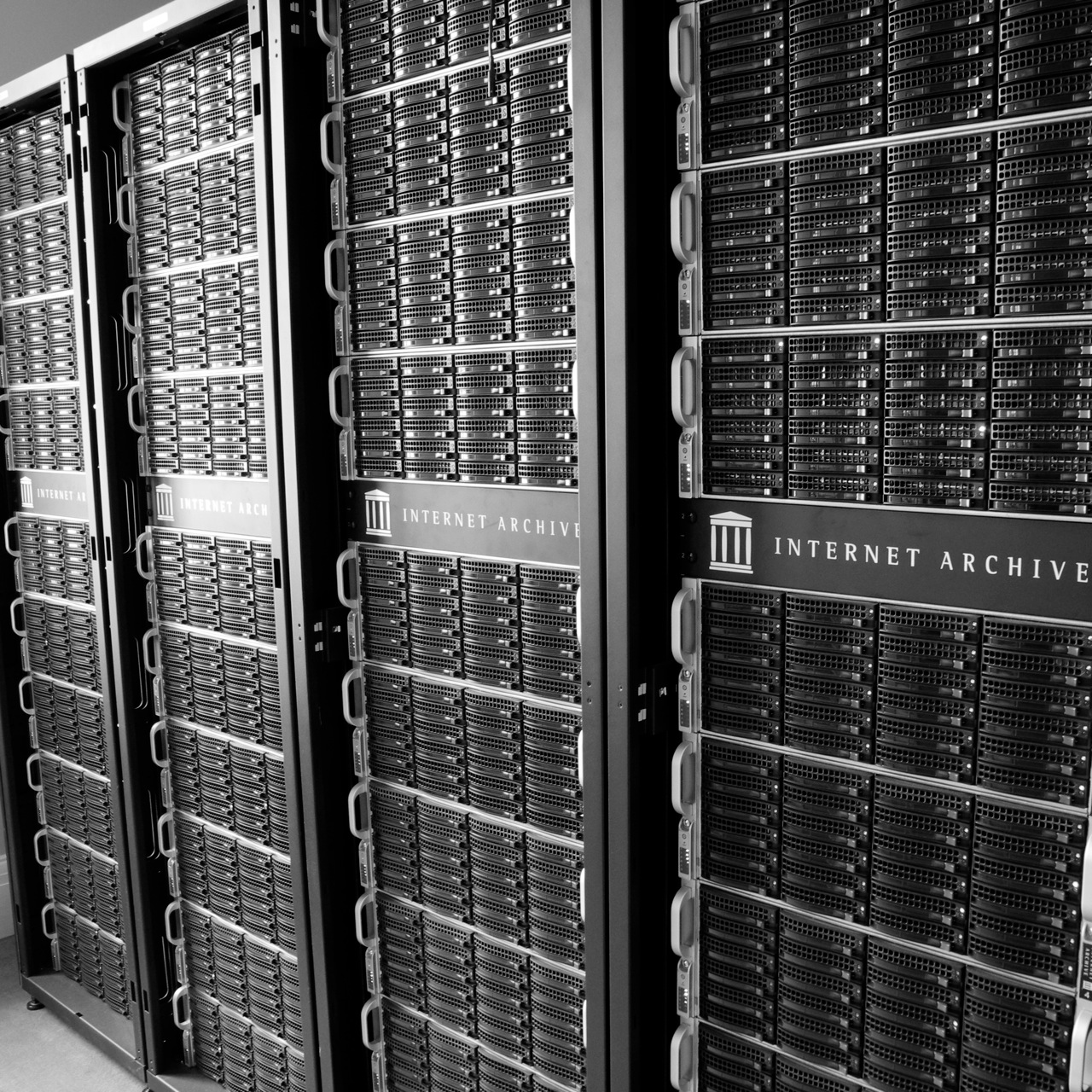

The current racks
Presenter Notes
Petabox 3

Presenter Notes
Shipping container

How big is the internet?
http://www.computerwoche.de/bild-zoom/1891307/1/489893/EL_12381492082557490680957/
Presenter Notes
Main services
- The site functions using three main pieces
- The locator
- The catalog
- The deriver
Presenter Notes
Locator service
- UDP packet sent out when a file needs to be downloaded.
- Server that holds that item responds.
- HTTP redirect to that server.
- Allows any number of storage nodes without much infrastructure change.
Presenter Notes
Catalog
- Offline task queue.
- Heart of the archives data processing operations.
- Time consuming modifications to data are done via. catalog tasks.
- Old fashioned message queue. Has tombstones from over half a decade ago.
Presenter Notes
Deriver
- Uploaded items are rsynced to a
worker. - Deriver taks run on them that create new files out of the originals.
- e.g.
ogg,mp3out ofFLACfiles. - OCR uploaded book scans to get the text out.
- e.g.
- New files created, metadata updated and item rsynced back to primary.
- Originals unmodified. Derivatives often more useful.
- Derivation is a catalog task.
Presenter Notes
Software stack
- PHP, Nginx, Solr, MySQL, Redis, solr and a pinch of Python and Java for the apps.
- KVM for virtualisation.
- Nagios, graphite, MRTG, cacti
Presenter Notes
What makes the Archive different?
Presenter Notes
Where would you store your data?
Where would you store your valuable data?
Presenter Notes
How would you store your data?
How would you store your valuable data?
Presenter Notes
The Approach
- Long term preservation
- Simplicity. Battle tested technologies.
- Independence and self-sufficiency.
- Low maintenance.
- Low cost.
- "Code dies, data lives on".
Presenter Notes
Thanks!
See us at the Internet Archive stall on the first floor.
http://archive.org/